What Is Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Cyber Threat Intelligence is the process of collecting, analyzing, and understanding information related to cyber threats to support better security decision-making. This information includes data about threats, threat actors, techniques used, and targeted victims. CTI aims to provide proactive insights so organizations can identify and prevent attacks before they occur.

CTI focuses not only on threat detection but also on the context behind those threats. By understanding who might attack, how they operate, and their objectives, organizations can develop more effective defense strategies.
Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence
CTI can be categorized into several types based on the type of information collected and its intended use:
- Strategic Threat Intelligence This type provides an overview of the threat landscape relevant to managerial decision-making. The data typically includes analysis of threat trends, motivations of threat actors, and potential future risks.
- Tactical Threat Intelligence Focused on techniques, tactics, and procedures (TTP) used by threat actors. This information is essential for technical security teams to detect and mitigate attacks.
- Operational Threat Intelligence Provides insights into specific ongoing threats, such as particular attack campaigns, new malware, or malicious activities on the network. This information is often obtained from the dark web or other intelligence sources.
- Technical Threat Intelligence Contains technical details such as malicious IP addresses, phishing domains, malware file hashes, and other indicators of compromise (IOC). This data is typically used to update security tools like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
Why Is Important?
CTI is increasingly vital in the cybersecurity ecosystem for several key reasons:
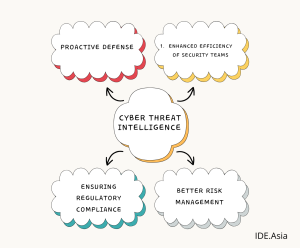
- Proactive Defense CTI enables organizations to take proactive actions based on identified threats rather than merely reacting after an attack has occurred. This helps minimize damage and reduce response time.
- Enhanced Efficiency of Security Teams With accurate information, security teams can focus their efforts on the most relevant threats, reducing information overload that often hinders threat detection.
- Better Risk Management Understanding the threats faced by an organization helps in managing risks more effectively, both technically and strategically.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance In some industries, compliance with data security regulations such as GDPR or PCI DSS is mandatory. CTI can help organizations ensure they remain compliant with these standards.
Key Components of Cyber Threat Intelligence
To produce effective threat intelligence, several key components must be part of the CTI process:
- Data Collection
Data is collected from various sources, including the dark web, hacker forums, system logs, and CTI service providers. Data sources must be reliable and relevant. - Data Analysis
Once collected, data must be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and threat indicators. This analysis can be done manually or using AI-based tools. - Contextualization
Analyzed data needs to be contextualized to ensure its relevance to a specific organization. For example, threats relevant to a tech company may differ from those affecting financial institutions. - Intelligence Delivery
Intelligence should be delivered in a format that stakeholders can understand and use, whether they are technical teams, managers, or executives.
Implementing Cyber Threat Intelligence
Implementing CTI requires a combination of tools, processes, and expertise. Here are the key steps in implementing CTI:
- Identify Needs
Determine the organization’s needs and objectives in using CTI. Is it to protect critical infrastructure, identify threat actors, or ensure regulatory compliance? - Select Appropriate Data Sources
Choose data sources relevant to the organization’s needs. These may include internal sources like security logs or external sources like third-party CTI services. - Use Suitable Tools
Invest in CTI tools such as Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIP) to automate data collection and analysis. - Integrate with Existing Security Systems
Ensure CTI outputs can be integrated with security tools like SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), firewalls, or endpoint detection and response (EDR). - Train Security Teams
Security teams must be trained to understand and utilize CTI effectively. This includes the ability to analyze data, recognize threat indicators, and take appropriate actions.
The Future of Cyber Threat Intelligence
As technology evolves, CTI will continue to adapt. Several trends are likely to shape the future of CTI:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Organizations will increasingly use AI and machine learning to quickly and accurately analyze threat data, reducing reliance on manual analysis.. - Global Collaboration
Organizations will collaborate more frequently to share threat data, creating a stronger defense network. - Focus on IoT Threats
With the increasing use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, threats to these devices will become a primary focus for CTI. - Process Automation
The processes of data collection and analysis will become more automated, enabling organizations to respond to threats faster.
Cyber Threat Intelligence is a critical element of modern cybersecurity strategies. By providing deep and contextual insights into threats, CTI helps organizations take proactive steps to protect their assets. While facing challenges, advancements in technologies like AI and global collaboration pave the way for a more efficient and effective CTI future.
For organizations aiming to stay competitive and secure in the digital era, investing in CTI is no longer an option but a necessity. With the right approach, CTI not only protects but also empowers organizations to thrive in an ever-changing threat landscape.