Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) is a technology that enables direct communication between the human brain and external devices, such as computers or prosthetics. In recent decades, advancements in neurotechnology have transformed BCI from a science fiction concept into a promising reality. With applications ranging from healthcare to entertainment, BCI has the potential to revolutionize the way humans interact with technology.

As research progresses, scientists are exploring ways to enhance the efficiency and reliability of BCI systems. Innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning are improving the accuracy of brain signal interpretation, making BCI applications more seamless and user-friendly. Additionally, ongoing studies aim to make non-invasive BCI technologies more effective, reducing the need for surgical interventions while maintaining high levels of precision.
Beyond its medical and entertainment applications, BCI could redefine the future of education and workplace environments. Imagine a scenario where students can interact with digital content using their thoughts or professionals can control complex machinery without physical movement. These advancements could open new possibilities for individuals with disabilities, enhancing accessibility and inclusivity in various industries.
How Brain-Computer Interfaces Works
BCI functions by capturing electrical signals generated by the brain and translating them into commands understandable by electronic devices. This process involves several key steps:
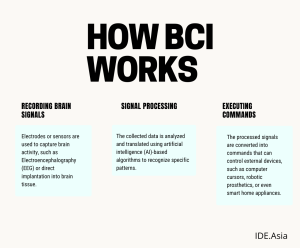
- Recording Brain Signals:
Electrodes or sensors are used to capture brain activity. For instance, this can be achieved through Electroencephalography (EEG) or, alternatively, by direct implantation into brain tissue. Moreover, both methods have their own advantages and challenges, requiring further research and development. - Signal Processing
The collected data is first analyzed and then translated using artificial intelligence (AI)-based algorithms to recognize specific patterns. Consequently, this process enhances accuracy and efficiency, allowing for more precise interpretations of neural signals.
- Executing Commands
The processed signals are converted into commands that can control external devices, such as computer cursors, robotic prosthetics, or even smart home appliances.
Current Applications of Brain-Computer Interfaces
BCI technology is already being utilized in various fields, including:
- Medical and Rehabilitation
BCI assists patients with motor impairments. For example, individuals with conditions such as ALS or stroke survivors can control prosthetic devices and wheelchairs using their thoughts. Moreover, this technology significantly enhances their independence and quality of life, making everyday tasks more manageable. - Gaming and Entertainment
The gaming industry is exploring BCI applications to create more immersive experiences, allowing players to control characters with their minds. - Alternative Communication:
Patients with conditions like locked-in syndrome can use BCI to type or communicate with the help of a computer. - Device Control
Some experiments have enabled individuals to control drones, robots, or smart home systems using BCI.
With advancements in AI, sensors, and neuromorphic computing, the future of BCI looks promising. Some anticipated developments include:
- Safer and More Effective Implants
The development of biocompatible materials and advanced surgical techniques may make invasive BCI safer and more acceptable. - Improved Resolution and Accuracy
More sophisticated machine learning algorithms will enhance real-time interpretation of brain signals. - Integration with Other Technologies
BCI could be combined with virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) to create more interactive and immersive experiences. - Greater Accessibility
As technology becomes more affordable, BCI could be more widely available to the general public, extending beyond medical and research environments.
Brain-Computer Interface is a revolutionary innovation that has the potential to transform human interaction with the digital world. Although there are still many challenges to overcome, the continuous advancement of this technology opens up new opportunities in medical, entertainment, and other fields.
With progress in AI, sensors, and neurotechnology, BCI may soon become an integral part of everyday life, bringing us closer to an era of truly connected human-machine interactions.